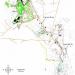
Cortez Mine Operations Permit Area
USA /
Nevada /
Battle Mountain /
World
/ USA
/ Nevada
/ Battle Mountain
World / United States / Nevada
mine, gold mine
The Cortez mine is located 100 kilometres southwest of Elko, Nevada in Lander County. The Cortez Pipeline property is 11 kilometres northwest and the Cortez Pediment property (which includes the Cortez Hills deposit) is 4 kilometres southeast of the original Cortez milling complex. The Pipeline and South Pipeline deposits are mined by conventional open-pit methods. The Cortez property covers approximately 2,800 square kilometres on one of the world’s most highly prospective mineral trends.
The Horse Canyon deposits were discovered in early 1976. Three pits, North, South, and South Extension were mined in the period from 1984 to 1987. Exploration drilling campaigns at the Horse Creek deposit, originally discovered in the late 1960s, occurred in the mid-1980s and intermittently over the last ten years and are ongoing.
The Pipeline deposit was discovered by CJV geologists in March 1991 during drilling of deep condemnation holes. The Gap deposit was discovered in 1991 adjacent to the planned Stage 9 of the Pipeline pit.
In November 1991 CJV discovered the South Pipeline deposit. Construction of Mill No. 2 and pre-stripping of the first stage of the Pipeline pit began in 1996. Continued drilling resulted in the 1998 discovery of the Crossroads deposit beneath 550 ft of alluvium
The Proven and Probable Mineral Reserve are estimated as of December 31, 2011.
• Proven and Probable Mineral Reserves total 306.9 million tons at a grade of 0.047 oz/st Au, containing 14.49 million ounces of gold.
• The Mineral Reserves are contained within five open pit deposits, two underground deposits, and surface stockpiles.
The Cortez Mine is a joint venture between two wholly owned subsidiaries of Barrick, Barrick Cortez Inc. (60%) and Barrick Gold Finance Inc. (40%). The Cortez operations consist of the Pipeline, Gap, Cortez and Cortez Hills open pits, the Cortez Hills underground mine, an 11,000 stpd carbon-in-leach (CIL) gold plant, heap leach pads and heap leach processing plants, the planned Crossroads open pit, and the Mineral Resources in the Cortez Hills underground mine and at the Hilltop exploration project.
Cortez Joint Venture which involved Placer Dome and Kenecott Barrick Gold acquired 60% in Cortez in 2006 when it purchased Placer Dome for US$10.4 billion, and acquired the remaining 40% from Rio Tinto in March 2008 for US$1.7 billion.[2]
Cortez employs three different metallurgical processes to recover gold. Lower-grade oxide ore is heap leached, while higher-grade non-refractory ore is treated in a conventional mill using cyanidation and a carbon-in-leach (“CIL”) process. Heap leached ore is hauled directly to leach pads for gold recovery. Carbonaceous mill ore is mined intermittently during the mining of the Pipeline/South Pipeline deposits. The Cortez Hills underground mine is accessed by twin declines portaled in the old Cortez Gold F canyon pit. The breccia ore zone employs underhand cut and fill mining methods with cemented rock fill as backfill. The top cut of the underground mine will eventually be the bottom bench of the Cortez Hills open pit.
With 2011 production of 1.42 million ounces at total cash costs of $245 per ounce1, Cortez is one of the world’s largest and lowest cost gold mines, and the property also has excellent upside exploration potential. Production in 2012 is anticipated to be 1.20-1.25 million ounces at total cash costs of $300-$350 per ounce1, reflecting a higher proportion of underground ounces and lower open pit grades as part of planned mine sequencing. Proven and probable mineral reserves at Cortez as of December 31, 2011 are 14.5 million ounces of gold2
www.barrick.com/GlobalOperations/NorthAmerica/Cortez/de...
www.infomine.com/minesite/minesite.asp?site=cortez
The Horse Canyon deposits were discovered in early 1976. Three pits, North, South, and South Extension were mined in the period from 1984 to 1987. Exploration drilling campaigns at the Horse Creek deposit, originally discovered in the late 1960s, occurred in the mid-1980s and intermittently over the last ten years and are ongoing.
The Pipeline deposit was discovered by CJV geologists in March 1991 during drilling of deep condemnation holes. The Gap deposit was discovered in 1991 adjacent to the planned Stage 9 of the Pipeline pit.
In November 1991 CJV discovered the South Pipeline deposit. Construction of Mill No. 2 and pre-stripping of the first stage of the Pipeline pit began in 1996. Continued drilling resulted in the 1998 discovery of the Crossroads deposit beneath 550 ft of alluvium
The Proven and Probable Mineral Reserve are estimated as of December 31, 2011.
• Proven and Probable Mineral Reserves total 306.9 million tons at a grade of 0.047 oz/st Au, containing 14.49 million ounces of gold.
• The Mineral Reserves are contained within five open pit deposits, two underground deposits, and surface stockpiles.
The Cortez Mine is a joint venture between two wholly owned subsidiaries of Barrick, Barrick Cortez Inc. (60%) and Barrick Gold Finance Inc. (40%). The Cortez operations consist of the Pipeline, Gap, Cortez and Cortez Hills open pits, the Cortez Hills underground mine, an 11,000 stpd carbon-in-leach (CIL) gold plant, heap leach pads and heap leach processing plants, the planned Crossroads open pit, and the Mineral Resources in the Cortez Hills underground mine and at the Hilltop exploration project.
Cortez Joint Venture which involved Placer Dome and Kenecott Barrick Gold acquired 60% in Cortez in 2006 when it purchased Placer Dome for US$10.4 billion, and acquired the remaining 40% from Rio Tinto in March 2008 for US$1.7 billion.[2]
Cortez employs three different metallurgical processes to recover gold. Lower-grade oxide ore is heap leached, while higher-grade non-refractory ore is treated in a conventional mill using cyanidation and a carbon-in-leach (“CIL”) process. Heap leached ore is hauled directly to leach pads for gold recovery. Carbonaceous mill ore is mined intermittently during the mining of the Pipeline/South Pipeline deposits. The Cortez Hills underground mine is accessed by twin declines portaled in the old Cortez Gold F canyon pit. The breccia ore zone employs underhand cut and fill mining methods with cemented rock fill as backfill. The top cut of the underground mine will eventually be the bottom bench of the Cortez Hills open pit.
With 2011 production of 1.42 million ounces at total cash costs of $245 per ounce1, Cortez is one of the world’s largest and lowest cost gold mines, and the property also has excellent upside exploration potential. Production in 2012 is anticipated to be 1.20-1.25 million ounces at total cash costs of $300-$350 per ounce1, reflecting a higher proportion of underground ounces and lower open pit grades as part of planned mine sequencing. Proven and probable mineral reserves at Cortez as of December 31, 2011 are 14.5 million ounces of gold2
www.barrick.com/GlobalOperations/NorthAmerica/Cortez/de...
www.infomine.com/minesite/minesite.asp?site=cortez
Wikipedia article: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cortez_Gold_Mine
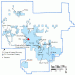
Nearby cities:
Coordinates: 40°11'57"N 116°41'14"W
- Phoenix Copper/Gold Project 58 km
- Emigrant Gold Mine 76 km
- Gold Quarry 77 km
- Genesis-Bluestar Operations Area 89 km
- Leeville Underground Project 89 km
- Ruby Hill Gold Mine 92 km
- Alligator Ridge Gold Mine 109 km
- Round Mountain 168 km
- Paradise Peak Mine 195 km
- Long Canyon Gold mine 201 km
- Pipeline Waste Rock Dump 4.2 km
- Area 30 Heap Leach Facility 4.3 km
- Pipeline Pit 5.7 km
- CHOP Waste Rock Facility 5.8 km
- Cortez Hills Pit 8 km
- Crescent Valley 26 km
- Grass Valley 34 km
- Tonkin Springs Mine 39 km
- Pinion Gold Project 65 km
- Diamond Valley 73 km