Gaibandha
Bangladesh /
Gaybanda /
World
/ Bangladesh
/ Gaybanda
/ Gaybanda
World / Bangladesh / Rajshahi / Ranpur / Gaibanda
town, third-level administrative division
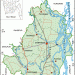
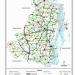
Gaibandha District (Rajshahi division) with an area of 2179.27 sq km, is bounded by Kurigram and Rangpur districts on the north, Bogra district on the south, Jamalpur, and Kurigram districts and Brahmaputra river on the east, Dinajpur and Rangpur districts on the west. Annual average temperature maximum 33.5°C, minimum 10.5°C; annual rainfall 2536 mm. Main rivers are Ghaghat, Karatoya, Bangali and Tista.
The location of Gaibandha town is 25.3284201N 89.5412085E. Gaibandha (Town) consists of 9 wards and 34 mahallas. The area of the town is 17.63 sq km. It has a population of 58362; male 51.14%, female 48.86%. This town was established in 1875 when the subdivision was transferred from Bhabaniganj to Gaibandha. Gaibandha municipality was established in 1923. Literacy rate among the town people is 61.9%.
Gaibandha district was established in 1984. The district consists of 7 upazilas, 3 municipalities, 27 wards, 82 union parishads, 1101 mouzas, 56 mahallas and 1244 villages. The upazilas are Fulchhari, Gaibandha sadar, Gobindaganj, Palashbari, Sadullapur, Sughatta and Sundarganj; the municipalities are Gaibandha Sadar, Gobindaganj and Sundarganj.
Archaeological heritage and relics: Vardhan Kuthi, Gobindaganj (17th century), house of Naldanga Zamindar along with its Shiva Linga made of black basalt, Vrisa Mandir of white stone and a large pond, Mosque of Shah Sultan Gazi at Mirer Bagan (1308),Mosque at Jamalpur, large pond at Faridpur, Masta Mosque at Gobindaganj.
Historical events: This region was a part of the Mourya, Pala, Gupta and Kamarupa kingdoms at different times. Movement was held in 1783 in this district against collection of excess taxes. Anti British movement (1921) and tebhaga movement (1946) were initiated in the district.
As of the 1991 Bangladesh census, Population 2117959; male 50.26%, female 49.74%; Muslim 91.29%, Hindu 7.79%, Christian 0.22%, Buddhist 0.13% and others 0.57%; ethnic nationals: Santal 861 families and Garo 227 families.
Religious institutions: Mosque 2999, temple 308, church 1, sacred place 6
Literacy and educational institutions: Average literacy 24.3%; male 31.6% and female 16.5%. Educational institutions: government college 3, non-government college 41, government high school 4, non-government high school 287, junior high school 31, madrasa 498, government primary school 737, non-government primary school 546, kindergarten 14, satellite school 83, community school 32, primary teacher's training institute 1, vocational training centre 1, agricultural training institute 1, B.Ed college 1, homeopath college 1. Noted educational institutions: Gaibandha Government High School (1885), Gaibandha Islamia High School (1914), Khodda Komorpur High School (1915), Tulshighat Kashinath High School (1917), Sadullapur Multilateral Pilot High school (1918), Bhorotkhali High School (1929), Palashbari SM Pilot High school (1919), Lakshmipur High School (1946), Gaibandha Government Girl's High School (1940), Gobindaganj Multilateral High School (1912), Belka MC High School (1918), Bamandanga MN High School (1917), Faridpur Government Primary School (1860) and Shivaram Government Primary School.
Cultural organisations: Club 124, public library 11, theatre group 25, cultural organisation 23, literary organisation 6, women's organisation 18, cinema hall 25 and theatre stage 6, opera party 10, Shilpakala academy 1, Shishu academy 1, children organisation 5, playground 61.
Main occupations: Agriculture 44.45%, agricultural labourer 27.72%, wage labourer 2.58%, transport 1.89%, commerce 9.11%, service 4.49% and others 9.76%.
Land use: Total cultivable land 149475 hectares, fallow land 67565.16 hectares; single crop 20.5%, double crop 58.5% and treble crop 21%; land under irrigation 27.16%.
Land control: Among the peasants 40% are landless, 35% small, 23% intermediate and 2% rich; cultivable land per head 0.07 hectare.
Main crops: Paddy, wheat, jute, sugarcane, potato, brinjal, mustard seed, chilli, onion, garlic and vegetables.
Main fruits: Mango, jackfruit, papaya, litchi, black berry, guava and banana.
Fisheries, dairies, poultries Poultry 277, diary 273, fishery 245, hatchery 5, nursery 16 and artificial cattle breeding centre 2.
Communication facilities Roads: pucca 365 km, semi pucca 93 km, mud road 3684 km; waterways 64 nautical mile; railways 54 km; flood protection dam 76 km.
Manufactories Sugar mill 1, cotton mill 1, flour mill 4, rice mill 40, biscuit factory 8, ice factory 28, soap factory 5, chira mill 2, plastic pipe factory 1, cold storage 1, saw mill 12, welding 28, hosiery 400.
Cottage industries: Total 5509; these include weaving, goldsmith, potteries, bidi, blacksmith, bamboo and cane work, tailoring, nakshi kantha, cocoon production, fishing net work, wood work.
NGO activities: Operationally important NGOs are brac, CARE, proshika, asa, Swanirvar Bangladesh, Ahsania Mission, Gana Unnayan Kendra, Thengamara Mahila Sabuj Sangha, Ekata, Ganaunnayan Kendra, Manab Unnayan Kendra and Ganakalyan Kendra
Health centres: Zila sadar hospital 1, upazila health complex 6, TB hospital 1, police hospital 1, prison hospital 1, village health centre 1, union health sub centre 33, maternity and child welfare centre 1, health and family welfare centre 66, MCH unit 3, satellite clinic 130, eye hospital 1 and community clinic 55.
The location of Gaibandha town is 25.3284201N 89.5412085E. Gaibandha (Town) consists of 9 wards and 34 mahallas. The area of the town is 17.63 sq km. It has a population of 58362; male 51.14%, female 48.86%. This town was established in 1875 when the subdivision was transferred from Bhabaniganj to Gaibandha. Gaibandha municipality was established in 1923. Literacy rate among the town people is 61.9%.
Gaibandha district was established in 1984. The district consists of 7 upazilas, 3 municipalities, 27 wards, 82 union parishads, 1101 mouzas, 56 mahallas and 1244 villages. The upazilas are Fulchhari, Gaibandha sadar, Gobindaganj, Palashbari, Sadullapur, Sughatta and Sundarganj; the municipalities are Gaibandha Sadar, Gobindaganj and Sundarganj.
Archaeological heritage and relics: Vardhan Kuthi, Gobindaganj (17th century), house of Naldanga Zamindar along with its Shiva Linga made of black basalt, Vrisa Mandir of white stone and a large pond, Mosque of Shah Sultan Gazi at Mirer Bagan (1308),Mosque at Jamalpur, large pond at Faridpur, Masta Mosque at Gobindaganj.
Historical events: This region was a part of the Mourya, Pala, Gupta and Kamarupa kingdoms at different times. Movement was held in 1783 in this district against collection of excess taxes. Anti British movement (1921) and tebhaga movement (1946) were initiated in the district.
As of the 1991 Bangladesh census, Population 2117959; male 50.26%, female 49.74%; Muslim 91.29%, Hindu 7.79%, Christian 0.22%, Buddhist 0.13% and others 0.57%; ethnic nationals: Santal 861 families and Garo 227 families.
Religious institutions: Mosque 2999, temple 308, church 1, sacred place 6
Literacy and educational institutions: Average literacy 24.3%; male 31.6% and female 16.5%. Educational institutions: government college 3, non-government college 41, government high school 4, non-government high school 287, junior high school 31, madrasa 498, government primary school 737, non-government primary school 546, kindergarten 14, satellite school 83, community school 32, primary teacher's training institute 1, vocational training centre 1, agricultural training institute 1, B.Ed college 1, homeopath college 1. Noted educational institutions: Gaibandha Government High School (1885), Gaibandha Islamia High School (1914), Khodda Komorpur High School (1915), Tulshighat Kashinath High School (1917), Sadullapur Multilateral Pilot High school (1918), Bhorotkhali High School (1929), Palashbari SM Pilot High school (1919), Lakshmipur High School (1946), Gaibandha Government Girl's High School (1940), Gobindaganj Multilateral High School (1912), Belka MC High School (1918), Bamandanga MN High School (1917), Faridpur Government Primary School (1860) and Shivaram Government Primary School.
Cultural organisations: Club 124, public library 11, theatre group 25, cultural organisation 23, literary organisation 6, women's organisation 18, cinema hall 25 and theatre stage 6, opera party 10, Shilpakala academy 1, Shishu academy 1, children organisation 5, playground 61.
Main occupations: Agriculture 44.45%, agricultural labourer 27.72%, wage labourer 2.58%, transport 1.89%, commerce 9.11%, service 4.49% and others 9.76%.
Land use: Total cultivable land 149475 hectares, fallow land 67565.16 hectares; single crop 20.5%, double crop 58.5% and treble crop 21%; land under irrigation 27.16%.
Land control: Among the peasants 40% are landless, 35% small, 23% intermediate and 2% rich; cultivable land per head 0.07 hectare.
Main crops: Paddy, wheat, jute, sugarcane, potato, brinjal, mustard seed, chilli, onion, garlic and vegetables.
Main fruits: Mango, jackfruit, papaya, litchi, black berry, guava and banana.
Fisheries, dairies, poultries Poultry 277, diary 273, fishery 245, hatchery 5, nursery 16 and artificial cattle breeding centre 2.
Communication facilities Roads: pucca 365 km, semi pucca 93 km, mud road 3684 km; waterways 64 nautical mile; railways 54 km; flood protection dam 76 km.
Manufactories Sugar mill 1, cotton mill 1, flour mill 4, rice mill 40, biscuit factory 8, ice factory 28, soap factory 5, chira mill 2, plastic pipe factory 1, cold storage 1, saw mill 12, welding 28, hosiery 400.
Cottage industries: Total 5509; these include weaving, goldsmith, potteries, bidi, blacksmith, bamboo and cane work, tailoring, nakshi kantha, cocoon production, fishing net work, wood work.
NGO activities: Operationally important NGOs are brac, CARE, proshika, asa, Swanirvar Bangladesh, Ahsania Mission, Gana Unnayan Kendra, Thengamara Mahila Sabuj Sangha, Ekata, Ganaunnayan Kendra, Manab Unnayan Kendra and Ganakalyan Kendra
Health centres: Zila sadar hospital 1, upazila health complex 6, TB hospital 1, police hospital 1, prison hospital 1, village health centre 1, union health sub centre 33, maternity and child welfare centre 1, health and family welfare centre 66, MCH unit 3, satellite clinic 130, eye hospital 1 and community clinic 55.
Nearby cities:
Coordinates: 25°19'53"N 89°31'40"E
- Meherpur District 180 km
- Chuadanga District 190 km
- Patran Tehsil 1440 km
- Tehsil Kallar Syedan 1819 km
- Bicholim Taluka 1949 km
- Pedne Taluka 1959 km
- Bardez Taluka 1963 km
- Garadagh district 4078 km
- Tegh Region 4315 km
- Meghri Municipality 4323 km
- Gaibandha District 8.7 km
- Shadullapur Upazlia HQ 9 km
- Fulchari Upazila HQ 10 km
- Shaghatta Upazila 21 km
- Pirganj 24 km
- Gobindaganj Upazila 26 km
- Rangpur District 45 km
- Kurigram District 49 km
- Rajshahi Division 59 km
- Dhaka Division 156 km