Garabogazköl
Turkmenistan /
Balkan /
Turkmenbasi /
World
/ Turkmenistan
/ Balkan
/ Turkmenbasi
World / Kazakhstan / Mangghystau
bay
Add category
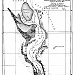
The Garabogazköl, alternatively the Kara-Bogaz-Gol (literally "mighty strait lake") is a shallow inundated depression in the northwestern corner of Turkmenistan. It forms a bay of the Caspian Sea with a surface area of about 7,000 mi² (18,000 km²). The translation "black strait lake" is a misunderstanding of the old Turkic name. It is separated from the Caspian, which lies immediately to the west, by a thin sandbar having a narrow opening through which the Caspian waters flow, cascading down into Garabogazköl. The water volume of the bay fluctuates seasonally with the Caspian Sea; at times it becomes a large bay of the Caspian Sea, while at other times its water level drops drastically.
For the first time in Kara-Bogaz-Gol belonged to a rowing lifeboat famous traveler, geographer and naturalist Greg Silych Karelin, who had worked in the Caspian Sea in 1832, 1834 and 1836 years.
Karelin had concluded that the observed strong currents of the Caspian Sea to the Kara-Bogaz-Gol is due to a lack in the Gulf of river flow, a very small amount of precipitation and evaporation is very strong, as indicated by FI Soymonov.
The first complete inventory (including soundings) Kara-Bogaz-Gola was made in 1847 by Lieutenant Ivan M. Zherebtsov included in this bay by boat "Volga". This Zherebtsov first noticed that when measuring the depth of the lot brought from the bottom is not the usual grounds, and "salt."
In order to definitively ascertain the impact of the Kara-Bogaz-Gola on the regime of the Caspian Sea, in particular to fisheries, in 1894, was organized expedition geologist NI Andrusova. However, the expedition failed. Her boat along with all the tools and the economy lost during the storm. Andrusov still gathered on the shores of the Gulf of collections of flora and fauna, including the bodies of fish recorded in the Kara-Bogaz Gol over from the Caspian Sea.
Satellite Andrusova, navigator Maksimović with the two sailors left to winter in the strait connecting the Caspian Sea to the Gulf of Kara-Bogaz-Gol, Turkmenistan to the boat and spent a very interesting observation. According to his records over to Kara-Bogaz-Hole there all year round, only a few oslabevaya winter. Status of fish passage to be terminated from November until mid-February, when water temperatures off the coast down to 10 ° and disappear Rachki serving fish food. Spring with the emergence of crustaceans on the passage down the vast amounts of fish of different breeds, but for her puppy.
In order to clarify and to supplement information obtained from Andrusova and Maximovich, Ministry of Agriculture, responsible at that time, fisheries, organized in 1897 a new expedition, which included hydrologist Spindler, Ostroumov zoologist, chemist and geologist Lebedintsev Andrusov. Marine Department provided the expedition paddle steamer "Krasnovodsk.
The big result of this expedition was the opening at the bottom of the Kara-Bogaz-Gola (the greatest depth of 13-14 m) layers glauberovoy salt. Salinity waters of Kara-Bogaz-Gola has been an average of about 164 0 / 00, but in some places reaches 200 0 / 00.
Further investigation showed that in summer when the temperature of bottom water rises to almost 30 °, much salt goes into solution. In winter, salt is deposited during the storm rolled ashore, forming its huge ramparts. About mirabilita shafts on the shores of the Kara-Bogaz-Gola wrote GS Karelin.
A more thorough, with the aim of fishing, a study of Kara-Bogaz-Gola were held in the XX century. Art describes the bay and its development under Soviet rule left Konstantin G. Паустовский lib.ru / PROZA / PAUSTOWSKIJ / karabugaz.txt
Until 1980, the Kara-Bogaz-Gol was extensive, almost closed the Gulf of the Caspian Sea.
Number of outliers on the surface rainfall is less than 200 mm and evaporation is 1400-1500 mm. In the water feeding the Kara-Bogaz-Gol is fully dependent on the inflow of Caspian waters through the narrow strait. Salinity of water in the bay reached 280-3050/00, was deposited mirabilita - a valuable commodity chemical that is produced in the Gulf for over 50 years.
As part of the solution to the problem of the Caspian Sea in order to slow down to reduce its level in 1980, Strait has been blocked deaf dam, the flow of Caspian waters in the Gulf ended. He was turned into a lake, almost devoid of water supply. Violation of the ecological balance is also affected the reduction of the reservoir due to evaporation. Already by 1983, its area decreased by 3 times (from 18 to 6 km2), the depth is not reached and 50 cm, the volume of brines decreased by 10 times, stopped mirabilita deposition, has been accumulated halite. In subsequent years, Kara-Bogaz-Gol has turned into a white salt desert. Raznosimye wind with the surface salts pollute the environment, causing soil salinity. Damage deposit mirabilita. There is a problem of Kara-Bogaz-Gola. To fix it, began to deliver the water from the Caspian Sea to the Kara-Bogaz-Gol in the pipes, then built a dam at the gateway to increase and regulate water delivery in the Kara-Bogaz-Gol.
In the Gulf of Kara-Bogaz-Gol concentrated brines huge reserves, which are excellent raw material for sodium sulfate, bischofite, epsomita.
stepnoy-sledopyt.narod.ru/geologia/kmore/priroda7.htm
For the first time in Kara-Bogaz-Gol belonged to a rowing lifeboat famous traveler, geographer and naturalist Greg Silych Karelin, who had worked in the Caspian Sea in 1832, 1834 and 1836 years.
Karelin had concluded that the observed strong currents of the Caspian Sea to the Kara-Bogaz-Gol is due to a lack in the Gulf of river flow, a very small amount of precipitation and evaporation is very strong, as indicated by FI Soymonov.
The first complete inventory (including soundings) Kara-Bogaz-Gola was made in 1847 by Lieutenant Ivan M. Zherebtsov included in this bay by boat "Volga". This Zherebtsov first noticed that when measuring the depth of the lot brought from the bottom is not the usual grounds, and "salt."
In order to definitively ascertain the impact of the Kara-Bogaz-Gola on the regime of the Caspian Sea, in particular to fisheries, in 1894, was organized expedition geologist NI Andrusova. However, the expedition failed. Her boat along with all the tools and the economy lost during the storm. Andrusov still gathered on the shores of the Gulf of collections of flora and fauna, including the bodies of fish recorded in the Kara-Bogaz Gol over from the Caspian Sea.
Satellite Andrusova, navigator Maksimović with the two sailors left to winter in the strait connecting the Caspian Sea to the Gulf of Kara-Bogaz-Gol, Turkmenistan to the boat and spent a very interesting observation. According to his records over to Kara-Bogaz-Hole there all year round, only a few oslabevaya winter. Status of fish passage to be terminated from November until mid-February, when water temperatures off the coast down to 10 ° and disappear Rachki serving fish food. Spring with the emergence of crustaceans on the passage down the vast amounts of fish of different breeds, but for her puppy.
In order to clarify and to supplement information obtained from Andrusova and Maximovich, Ministry of Agriculture, responsible at that time, fisheries, organized in 1897 a new expedition, which included hydrologist Spindler, Ostroumov zoologist, chemist and geologist Lebedintsev Andrusov. Marine Department provided the expedition paddle steamer "Krasnovodsk.
The big result of this expedition was the opening at the bottom of the Kara-Bogaz-Gola (the greatest depth of 13-14 m) layers glauberovoy salt. Salinity waters of Kara-Bogaz-Gola has been an average of about 164 0 / 00, but in some places reaches 200 0 / 00.
Further investigation showed that in summer when the temperature of bottom water rises to almost 30 °, much salt goes into solution. In winter, salt is deposited during the storm rolled ashore, forming its huge ramparts. About mirabilita shafts on the shores of the Kara-Bogaz-Gola wrote GS Karelin.
A more thorough, with the aim of fishing, a study of Kara-Bogaz-Gola were held in the XX century. Art describes the bay and its development under Soviet rule left Konstantin G. Паустовский lib.ru / PROZA / PAUSTOWSKIJ / karabugaz.txt
Until 1980, the Kara-Bogaz-Gol was extensive, almost closed the Gulf of the Caspian Sea.
Number of outliers on the surface rainfall is less than 200 mm and evaporation is 1400-1500 mm. In the water feeding the Kara-Bogaz-Gol is fully dependent on the inflow of Caspian waters through the narrow strait. Salinity of water in the bay reached 280-3050/00, was deposited mirabilita - a valuable commodity chemical that is produced in the Gulf for over 50 years.
As part of the solution to the problem of the Caspian Sea in order to slow down to reduce its level in 1980, Strait has been blocked deaf dam, the flow of Caspian waters in the Gulf ended. He was turned into a lake, almost devoid of water supply. Violation of the ecological balance is also affected the reduction of the reservoir due to evaporation. Already by 1983, its area decreased by 3 times (from 18 to 6 km2), the depth is not reached and 50 cm, the volume of brines decreased by 10 times, stopped mirabilita deposition, has been accumulated halite. In subsequent years, Kara-Bogaz-Gol has turned into a white salt desert. Raznosimye wind with the surface salts pollute the environment, causing soil salinity. Damage deposit mirabilita. There is a problem of Kara-Bogaz-Gola. To fix it, began to deliver the water from the Caspian Sea to the Kara-Bogaz-Gol in the pipes, then built a dam at the gateway to increase and regulate water delivery in the Kara-Bogaz-Gol.
In the Gulf of Kara-Bogaz-Gol concentrated brines huge reserves, which are excellent raw material for sodium sulfate, bischofite, epsomita.
stepnoy-sledopyt.narod.ru/geologia/kmore/priroda7.htm
Wikipedia article: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Garabogazköl
Nearby cities:
Coordinates: 41°22'53"N 53°45'46"E
- Gulf Kendirli 182 km
- Kaydak gulf 435 km
- Bay Butakova 808 km
- Bay Saryshyganak 838 km
- Old Bay 1342 km
- New Bay 1342 km
- Railway border station Bolashak-Export 105 km
- Possible Border Outpost 112 km
- Possible Border Outpost 137 km
- Ruins 156 km
- Ustyurt Nature Reserve 163 km
- Chink Kaplankyr 167 km
- Kumesebšek Key 170 km
- Kazahlışor 181 km
- Sands of Kumesebshen 182 km
- Depression Assake Audan 252 km







Comments